
Assuming constant acceleration g due to Earth’s gravity, Newton's law of universal gravitation simplifies to F = mg, where F is the force exerted on a mass m by the Earth’s gravitational field of strength g.
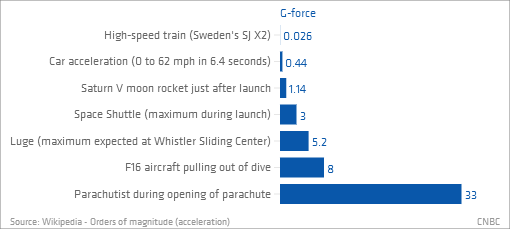
Though the term “zero gravity” is sometimes used to describe the free-falling conditions during space flight on the orbit around the Earth, gravity of course still exists in any spacecraft. The wings are strengthened so that the aircraft can withstand accelerations up to 2G. During the modification, the fuel, hydraulic, and some other systems are improved to ensure their normal operation under conditions of short-term weightlessness. In Europe, Airbus A310 is used by the National Centre for Space Studies. Various airplanes were used for zero-gravity research: modified Tupolev Tu-104AK, Tu-134LK, Tu-154MLK, and Ilyushin Il-76MDK in the Soviet Union and Russia since 1961, modified AJ-2, C-131, KC-135, and Boeing 727-200 in the USA since 1959. During short periods of time, about 25 seconds in every minute of flying, the aircraft does not exert any reaction force on people inside causing the sensation of weightlessness. The plane flights on a ballistic parabolic flight path. Reduced-gravity aircraft were used in several countries to provide a brief weightless environment for training astronauts and conducting various experiments. On the surfaces of other planets and astronomical bodies, the gravitational acceleration is different. If gravity is the only influence acting upon various objects and there is no air resistance, the acceleration is the same for all objects and is equal to the gravitational acceleration of 9.8 meters per square second (m/s²) or 32.2 feet per square second (ft/s²) on the surface of the Earth.

G FORCE CALCULATOR FROM DISTANCE OVER SECONDS FREE
Objects falling on the ground at low speed can be considered being in free fall because in this case the air resistance is negligible and can be neglected. Planets orbiting the Sun are also in free fall. For a body that falls in a vacuum, however, gravity is the only force acting upon it.Įxamples of free fall are spacecraft and satellites orbiting the Earth because the gravity of the Earth is the only force acting upon them. If an object falls through an atmosphere, an additional drag force is acting upon it and its motion depends not only on gravitational acceleration but also on its mass, cross-sectional area, and other factors. In classical mechanics, the state of an object that freely moves in the presence of gravity is called free fall. Inside Soyuz TMA-19M descent module on display at the Science Museum, London Definitions and Formulas


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
